Conventional vs Inverter Generators: What’s the Difference?
-
- Last updated:


You might not use a generator every day, but when you do, you’ll thank yourself profusely for investing in one. It will provide much-needed electricity to make sure you can power your home, RV, appliances, and devices. However, there are some radical differences between the various types.
There are three kinds of generators, based on their performance. They include:
- Conventional
- Inverter
- Solar
We’ll focus on the first two, with a detailed look at the pros and cons that each one brings to the table. There are two ways to approach this decision. You can consider it strictly from a feature perspective. You can also think about your intended use to guide your purchases. We’ll discuss both ways to help you arrive at an informed choice.

Overview of a Conventional Generator
Both a conventional and inverter generator operate under the same principle. They use an engine powered by a fuel source to convert energy from one form to another. In this case, it is mechanical going to electricity. They do this with an alternator, which handles the business end of producing alternating current (AC) to run your stuff.
The framework for the conventional generator goes back to Michael Faraday and his invention of the Faraday disk in 1831. The first fuel-driven models followed, propelled by technological advances during World War I and II. It’s the key point that separates the conventional from the inverter generator. It produces AC power directly. You can consider it the first-generation of modern-day electricity generation.
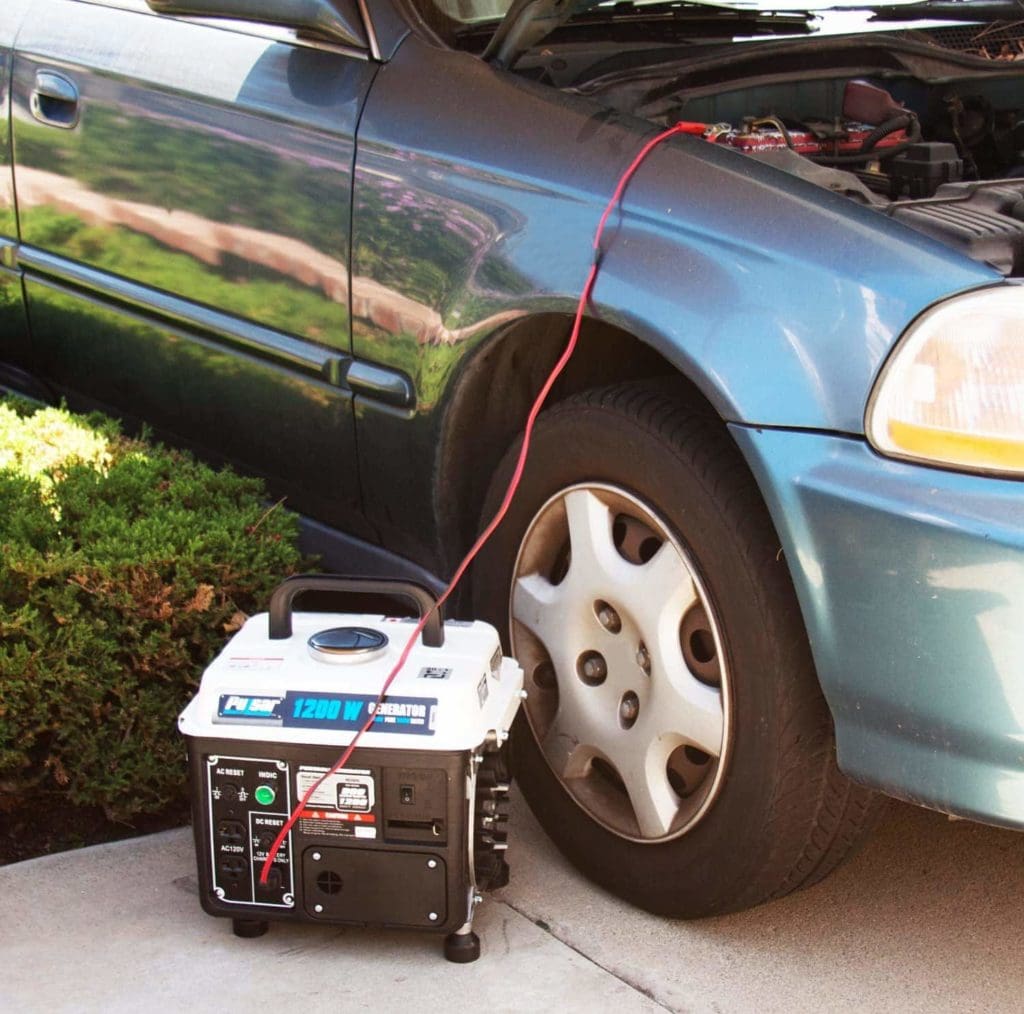

How It Works
A conventional generator uses either propane, gasoline, or diesel to supply the power to do the energy conversion to electricity via the alternator. Some models use a dual-fuel system, with propane often acting as the secondary source. A voltage regulator keeps it running on an even keel. This type of generator will emit fumes just like your car or lawnmower. The larger the model, the more electricity it will produce.
When to Choose It
The conventional generator succeeds when it comes to a versatile product with a high-power output. That makes it an excellent choice for contractors who need a reliable electricity source on the job. It’s also a great option if you’re looking for an emergency backup system for your home. It can deliver the power you need at decent runtimes.
Noise Level
The noise level is where the pedal meets the metal with a conventional generator. The power comes at a price, which in this case, is a higher noise level. You’ll find this information listed with the specs of the product. The figure is typically from about 20 inches away from the device. Most will run over 60 decibels (dB), with some approaching 75 dB.
For comparison, the latter figure is about the same as a vacuum cleaner. It’s worth noting that levels over 85 dB are putting you in the danger zone. We suggest that you use this spec in your decision-making process for comparison. Bear in mind that it can affect your usage of the generator.
Portability
The type of fuel your generator uses plays a direct role in its portability. A gallon of gasoline weighs about 6 pounds. On the other hand, diesel comes in at just over 7 pounds, whereas a propane tank can weigh anywhere from 4 pounds or more. Therefore, the fuel type is a vital consideration with these products. It also makes a built-in handle and wheels a godsend.
Power
The conventional generator succeeds when it comes to power. It’s typically a function of the size of the tank and the output. Another factor in its favor is its runtime, which is optimal with these models. That makes them a smart choice for longer projects for which you’ll need a lot of juice to complete. Most generators run at least 3600 RPM, which is adequate to start up and power most appliances requiring 120 volts.
The conventional generator can push those limits to 10,000 watts, which makes them excellent choices for running multiple power tools on a job site. However, more juice also means a greater weight. Products capable of this output are beasts.
Performance
Another factor differentiates conventional and inverter generators based on the latter’s newer technology. The one glaring drawbacks of a conventional generator is its inability to maintain a steady RPM. Instead, it fluctuates, known as harmonic distortion in the industry. You may see it described as a lack of clean electricity. It may not matter as much for your power tools, but it can take out sensitive devices like computers.
- High power outputs
- Long runtimes
- More affordable
- More maintenance
- Not clean electricity
- Heavy and sometimes less portable
- Noisy
Overview of an Inverter Generator
An inverter generator builds on the principles of the conventional type, but it arrives at the final destination via a different route. One of the main differences between the two kinds is the running speed. A conventional model stays at its fixed point. On the other hand, an inverter is more adaptable to the varying energy demands. That factor comes into play in the main concepts we considered with the former.
Honda introduced the newer technology of the inverter generation in 1965. It was a significant breakthrough that made these products more accessible to residential households. They addressed the downsides of operating a conventional generator, making them the preferred choice for many consumers.
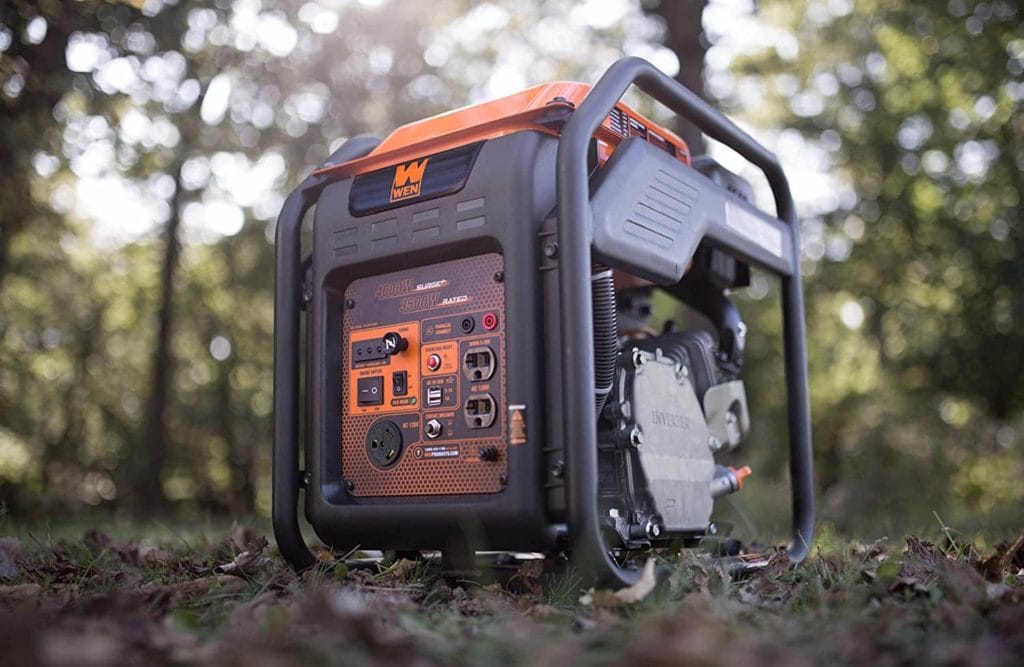

How It Works
The operation of an inverter generator may sound counterproductive at first glance. Instead of going directly to AC power, this device takes AC to DC and then back again via an inverter, hence, the name. That mechanism achieves one significant milestone—a steadier flow of electricity. That factor plays a critical role in which type of generator you should choose.
When to Choose It
The more stable output makes an inverter generator a smart choice if you’re running sensitive devices, such as computers, tablets, or smartphones. The steady current is less likely to damage the circuitry when compared to the fluctuating delivery of a conventional generator. The reason is that there is considerably less harmonic distortion with these models.
Noise Level
Another benefit of the inverter generator is its quieter noise levels. You’ll find products that are considerably less noisy, going down to 60 dB or less. That’s about the same as normal conversation. You won’t have to scream over a running device. That can make them better choices if you use one to run your RV. Your fellow campers will thank you for it.
Portability
The inverter generator is more portable than a conventional one. They are more lightweight and less bulky. Whether a product has built-in wheels is less of a consideration if it’s light enough to carry by its handle. That will also make storage between uses less of a hassle. Fuel is another factor that affects the weight and usability of these products, which we’ll discuss later in this piece.
Power
A conventional generator takes the top prize if you need a powerful device. The inverter generator can’t match the former’s higher output. You can find models that can push 4000 watts, but that comes at a higher price tag and blurring of the other benefits that this type offers. A critical difference is how the inverter generator metes out electricity. Its output varies with the demand, which directly affects its operation.
Performance
One of the main benefits of the inverter generator is its superior fuel efficiency. You can get more juice with less fuel. That, in turn, cuts down on its weight and increases its portability. It also makes these products more environmentally friendly than conventional ones that emit more fumes.
- More fuel-efficient
- Less noisy
- Less maintenance
- Compact size
- More expensive
Buyer’s Guide for Generators
A generator is a significant investment, whether you choose a conventional one over an inverter. We suggest that the first place to start is with your power needs.
If you plan to use it for DIY projects, think about the number and types of power tools you’ll likely run. Likewise, calculate what you’ll need to power the appliances, lights, and devices in your RV or home in the case of a backup electricity source. Crunching the numbers is a must-do to choose a generator that will deliver optimal performance when you need it most.
Other Factors to Consider
As you’ve learned, fuel type is a vital consideration on several scores. However, we’d also suggest taking it to the next level. For example, think about the availability of fuel if you’re boondocking versus a stationary emergency backup system at home.
Price
Price is another critical factor, especially if the output is an issue. The conventional generator delivers the goods at a more affordable cost. However, you can get more power with inverter generators that support parallel connections. That also brings versatility to the table. You can take one or more devices with you, depending on your power needs.
Bear in mind the total cost of owning a generator. The inverter will dip into your pocketbook more at the onset. However, it will run more efficiently. Likewise, a conventional model may cost less upfront but take a greater toll on fuel and maintenance over time.
Convenience
Of course, convenience is always something you must think about, too. Inverter generators are more portable, which can put them in the dealmaker category for an RV. They also require less maintenance than a conventional generator. However, if there are frequent outages in your area, it’s hard to beat the long running times and optimal power of a conventional generator.
Fuel plays another role with convenience. If you use your generator for fair-weather camping trips, the fuel type isn’t as vital of a consideration. If you camp year-round, you’ll likely find that propane isn’t the best choice as a primary source. The same thing applies to using your generator as a backup if you live in a northern climate.
Environmental Impact
A generator running on fossil fuels has an unavoidable environmental cost. Fortunately, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates these products for their fuel efficiency and operation. Many manufacturers have also opted for the stricter California CARB-Compliant requirements, making them an even more eco-friendly choice.

Final Thoughts
The question of whether you choose a conventional over an inverter generator often rests on two factors: noise and output. If quiet operation is a dealmaker for you, an inverter generator is a wiser investment. On the other hand, a conventional generator delivers more power with longer runtimes. Price and convenience are also vital considerations that can point you in the right direction. It begins with understanding your power needs.
Contents

